Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) is a widely used method for assessing body composition and overall health. This non-invasive technique measures the resistance of electrical currents as they pass through the body. In this blog, we will explore the ins and outs of BIA, including how it works, what it measures, who can benefit from it, its accuracy, different types of BIA, as well as its advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, we will take a look at the various devices used for BIA.
How does Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Work?
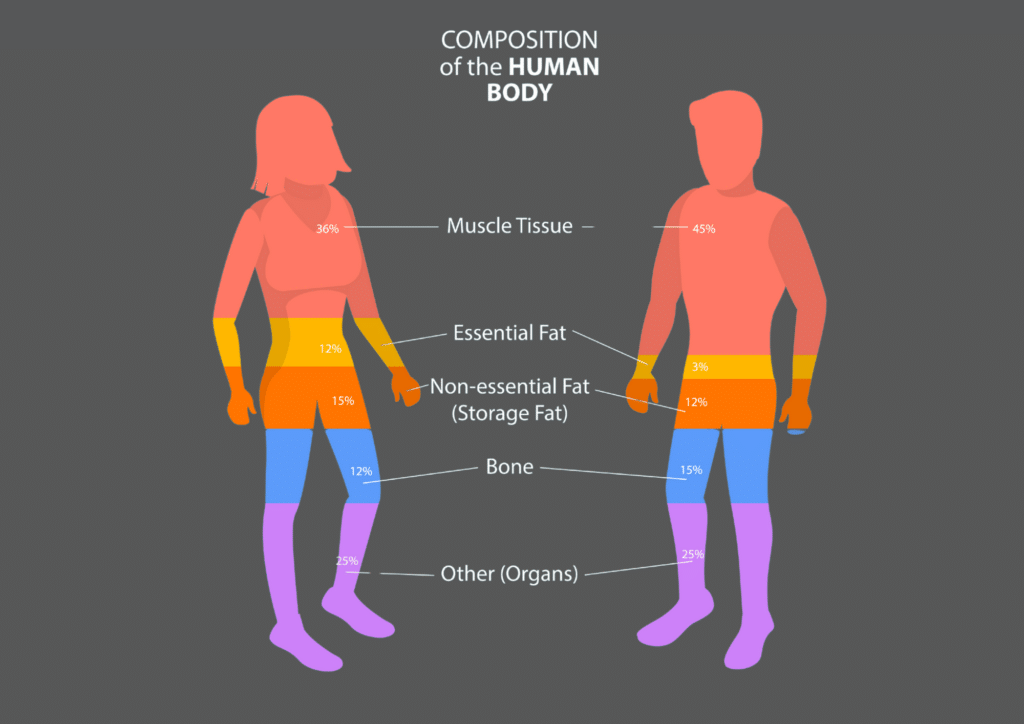
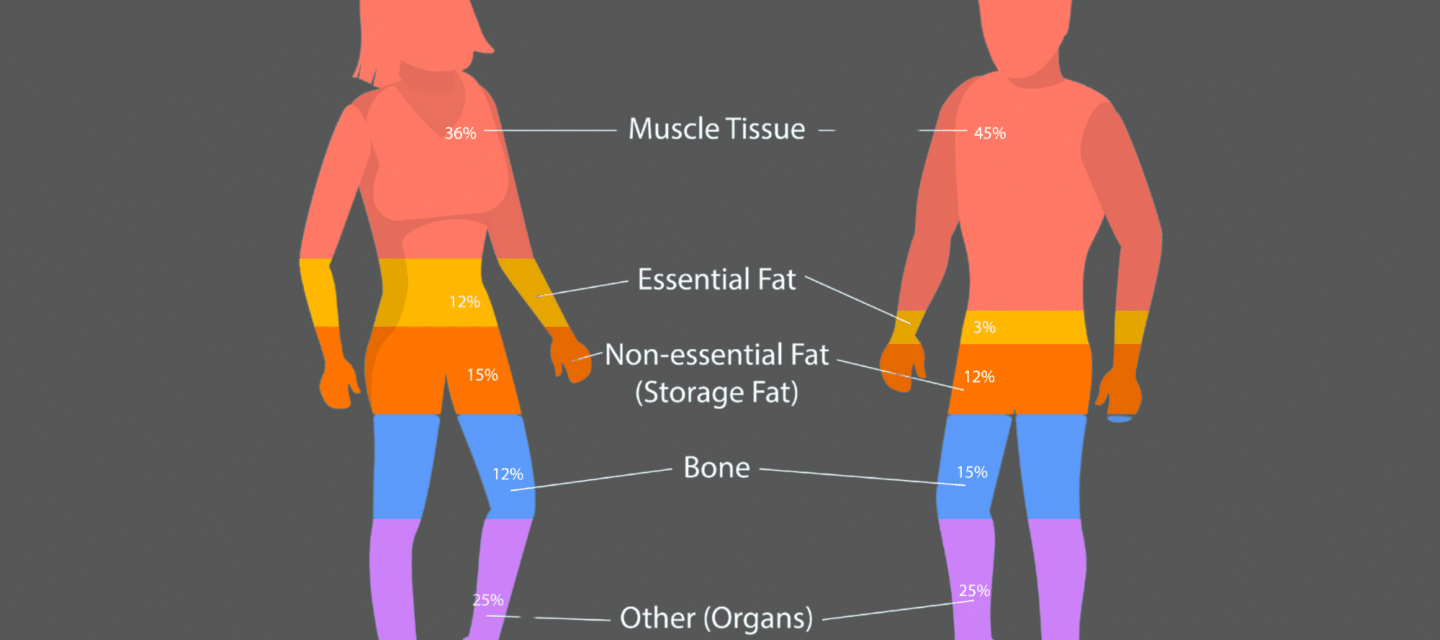
BIA works on the principle that different tissues in the human body conduct electrical currents differently. Lean body mass, which includes muscles, blood, and organs, contains a high water and electrolyte content and conducts electricity well. Fat, on the other hand, has less water and electrolyte content and conducts electricity poorly. BIA devices send a low-level electrical current through the body, and by measuring the resistance (impedance) to this current, they can estimate various body composition parameters.
What Does Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Measure?
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) measures several key parameters related to body composition and overall health. These measurements include:
- Body Fat Percentage: BIA estimates the proportion of your total body weight that is composed of fat. It’s a valuable metric for assessing body composition and is used in fitness and healthcare settings to track changes in fat mass.
- Lean Body Mass: BIA provides an estimate of your lean body mass, which includes muscle, bone, blood, and organs. This measurement is essential for evaluating muscle mass and overall health.
- Total Body Water: BIA assesses your body’s water content, which includes both intracellular and extracellular water. Monitoring total body water is important for hydration status and overall well-being.
- Metabolic Rate: Some advanced BIA devices can estimate your resting metabolic rate (RMR), which is the number of calories your body needs to maintain basic functions at rest. This information is useful for weight management and dietary planning.
- Segmental Analysis: Some BIA devices can provide segmental analysis, which assesses the composition of specific body segments, such as arms, legs, and the trunk. This can help identify imbalances or asymmetries in muscle development.
- Visceral Fat: Certain BIA devices can estimate the amount of visceral fat, which is the fat stored around the internal organs in the abdominal cavity. High levels of visceral fat are associated with an increased risk of various health conditions.
- Phase Angle: Phase angle is a parameter that reflects the integrity of cell membranes and the overall health of cells. It can provide insights into cellular health and nutritional status.
Who is it for?
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) is a versatile method for assessing body composition and overall health, and it can be beneficial for a wide range of individuals, including:
- Fitness Enthusiasts: BIA is commonly used by individuals who are interested in fitness and body composition. It helps them track changes in body fat percentage, lean muscle mass, and other key parameters. This information is valuable for setting and monitoring fitness goals, such as losing weight, gaining muscle, or improving overall body composition.
- Athletes: Athletes, both professional and amateur, often use BIA to monitor their body composition and make informed decisions about their training and nutrition plans. It can help them optimize their performance and ensure they maintain the right balance of muscle and fat. It can also be used to determine hydration status.
- Healthcare Professionals: BIA is a useful tool for healthcare providers, including doctors, dietitians, and physical therapists. It is used to assess patients’ body composition and hydration status, particularly in individuals with conditions like obesity, diabetes, kidney disease, and heart failure or other cardiovascular diseases. They can also use BIA to tailor dietary recommendations to their patients specific needs. It helps them create personalized nutrition and diet plans based on an individual’s body composition and metabolic rate.
- Research and Studies: BIA is used in scientific research and clinical studies to gather data on body composition changes in various populations, helping researchers understand the relationship between body composition and health.
- Individuals with Special Health Concerns: BIA can be particularly useful for individuals with specific health concerns, such as those with chronic conditions or those recovering from surgery or injury. It helps assess changes in body composition during the healing and recovery process.
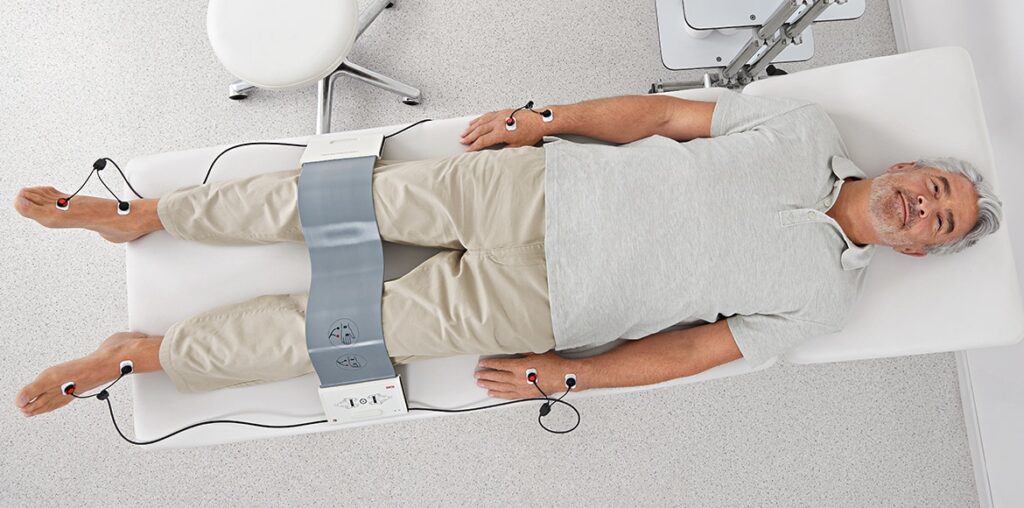
How Accurate Is Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis?
BIA provides a reasonably accurate estimate of body composition when used correctly. However, its accuracy can be affected by various factors, including hydration status, the quality of the BIA device, and individual characteristics. For precise measurements, it’s essential to follow standardized procedures and use high-quality BIA equipment.
Types of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
There are two primary types of BIA:
- Single-Frequency BIA (SF-BIA): This method uses one low-frequency electrical current to measure impedance. It is commonly found in home scales and handheld devices.
- Multi-Frequency BIA (MF-BIA): MF-BIA uses multiple electrical frequencies to measure impedance at different depths within the body. It is generally more accurate and is often used in clinical settings.

Advantages & Disadvantages of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
Advantages
- Non-invasive: BIA does not require needles or invasive procedures.
- Quick and easy: BIA measurements are fast and can be performed in various settings.
- Useful for tracking changes: BIA is valuable for monitoring progress in fitness and weight management programs.
Disadvantages
- Sensitivity to factors: BIA measurements can be influenced by factors like hydration, food intake, and exercise.
- Variable accuracy: The accuracy of BIA can vary between devices and individuals.
- Limited precision: While BIA provides a good estimate of body composition, it may not be as precise as other methods like DEXA scanning, which is often seen as the ‘gold standard method’ of measuring body composition.
Devices for Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
There are several devices used for BIA, ranging from simple bathroom scales with built-in BIA functionality to more advanced professional-grade equipment found in clinical settings.
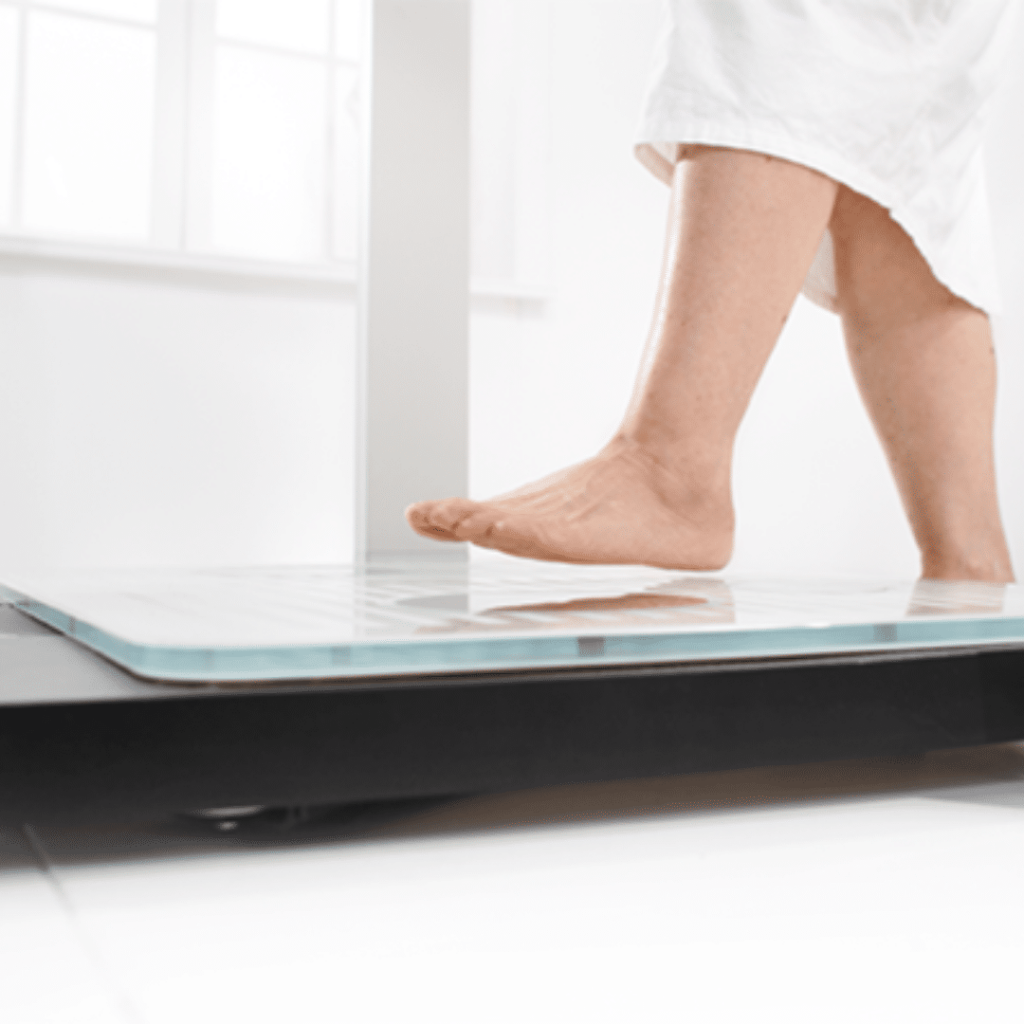
Bathroom Scales: Many home bathroom scales now come equipped with BIA functionality.
Medical scales: In medical and clinical settings, advanced BIA equipment is used for precise assessments of body composition and hydration status in patients with specific health conditions. These machines are operated by trained professionals to ensure accurate results.
Handheld Devices: Portable BIA devices that are easy to use and suitable for personal use or small clinics. They are also used by fitness enthusiasts, atheletes and personal trainers. Users hold the device and follow the instructions to measure body composition. These devices can provide more accurate measurements than bathroom scales.

seca mBCA 525 Body Composition Analyser
The seca mBCA 525 is a portable, 8-point Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) Analyser for determining body composition in a lying position.
Professional BIA Machines: High-end BIA machines found in medical facilities and fitness centers, offering more accurate and comprehensive measurements.
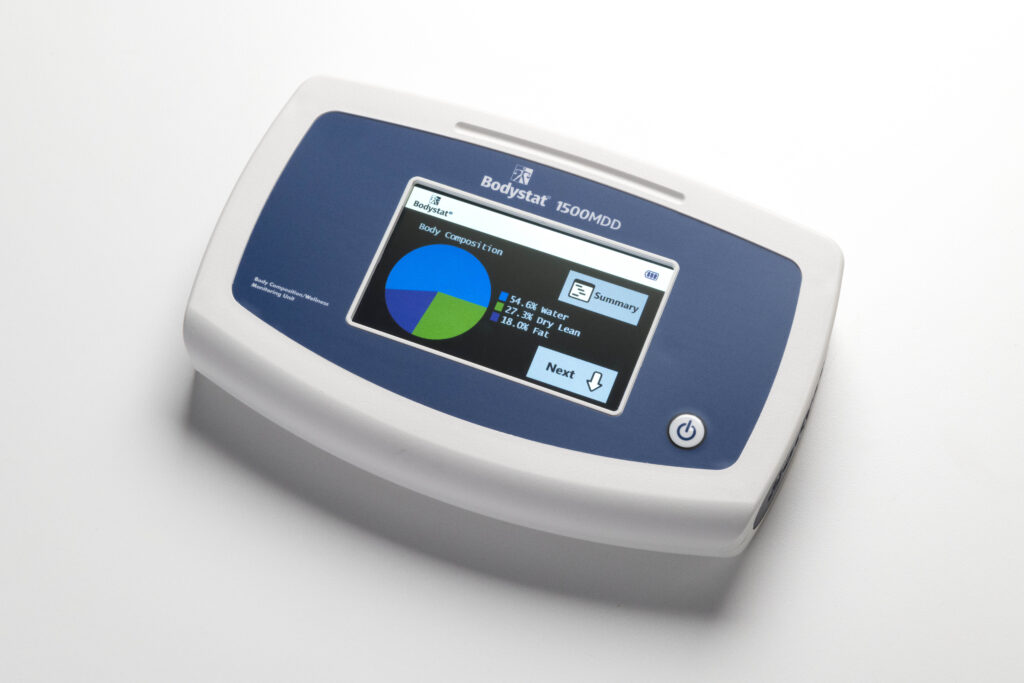
Bodystat 1500 MDD
The Bodystat 1500 MDD is a lightweight, hand-held, battery operated Bio-impedance Analyser which is easy to use and requires no specialist skills.
It’s a non-invasive body composition and wellness monitoring device that provides a quick, full analysis of cellular health, nutrition status and overall health and fitness of the person being monitored.
The Bodystat 1500 MDD measures bio-impedance on a whole body basis rather than just the limbs to provide a greater accuracy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis is a versatile method for assessing body composition and health. While it has its limitations, it can be a valuable tool for individuals, healthcare professionals, and fitness enthusiasts looking to monitor and manage their body composition and overall well-being. When using BIA, it’s essential to consider the factors that may affect its accuracy and follow best practices for reliable results.













2 thoughts on “A Comprehensive Guide to Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)”